Green Beans
Legume
Age Suggestion
6 months
Iron-Rich
No
Common Allergen
No

When can babies have green beans or string beans?
Green beans, sometimes known as string beans, may be introduced as soon as baby is ready to start solids, which is generally around 6 months of age.
Green beans are snap beans—a sprawling family of legumes whose tender pods are eaten before their tiny seeds mature and swell from soaking up sun and water. Aside from green beans, there are bush beans, pole beans, string beans, and wax beans, to name a few. All trace back to the common bean that was cultivated by Indigenous people of Central and South America for thousands of years before colonizers took the seeds to Europe.
Are green beans healthy for babies?
Yes. Green beans are an excellent source of vitamin K—an essential nutrient that plays a key role in blood clotting. They also contain vitamin A (for healthy eyesight and immune systems) and vitamin C, a critical nutrient that helps our bodies absorb iron from plant-based foods, which is important for babies at this stage in their lives. Lastly, green beans help fuel baby’s body with protein and move things along in the digestive tract thanks to plenty of fiber within the tender pods.
Are green beans a common allergen?
No. Green bean allergies are rare, though not unheard of and, in theory, an individual can be allergic to any food. As you would when introducing any new food, start by offering a small quantity on its own for the first few servings. If there is no adverse reaction, gradually increase the quantity over future meals.
Are green beans a choking hazard for babies?
Yes. Green beans can be firm and, when cut into small sizes, are similar in size and shape to the trachea at this early stage in life, qualities that increase the risk of choking. To reduce the risk, prepare and serve green beans in an age-appropriate way as described in the How to Serve section. Worried about the small beans inside each pod? The act of munching on a green bean pod tends to smash and flatten the little beans inside, which decreases choking risk. You can also use the back of a fork to flatten the whole cooked green bean pod before offering to baby to further decrease the risk. As always, make sure you create a safe eating environment and stay within an arm’s reach of baby during meals.
Learn the signs of choking and gagging and more about choking first aid in our free guides, Infant Rescue and Toddler Rescue.
Videos
Do I need to worry about the nitrates in green beans?
No, there is no need to worry. You may have heard that green beans and other vegetables (like arugula, beets, carrots, lettuce, spinach, and squash to name a few) contain nitrates, which are naturally-occurring compounds which, if consumed in large amounts, may negatively affect oxygen levels in the blood. Babies younger than 3 months of age and/or those with health concerns may be more susceptible to the effects of nitrates. Organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the European Food Safety Authority view nitrates in vegetables as generally not a concern for most healthy children and that the benefits of eating these vegetables as part of a varied diet typically outweigh the risks of excess nitrate exposure.
How do you serve green beans to babies?
Every baby develops on their own timeline, and the suggestions on how to cut or prepare particular foods are generalizations for a broad audience.
6 months old +:
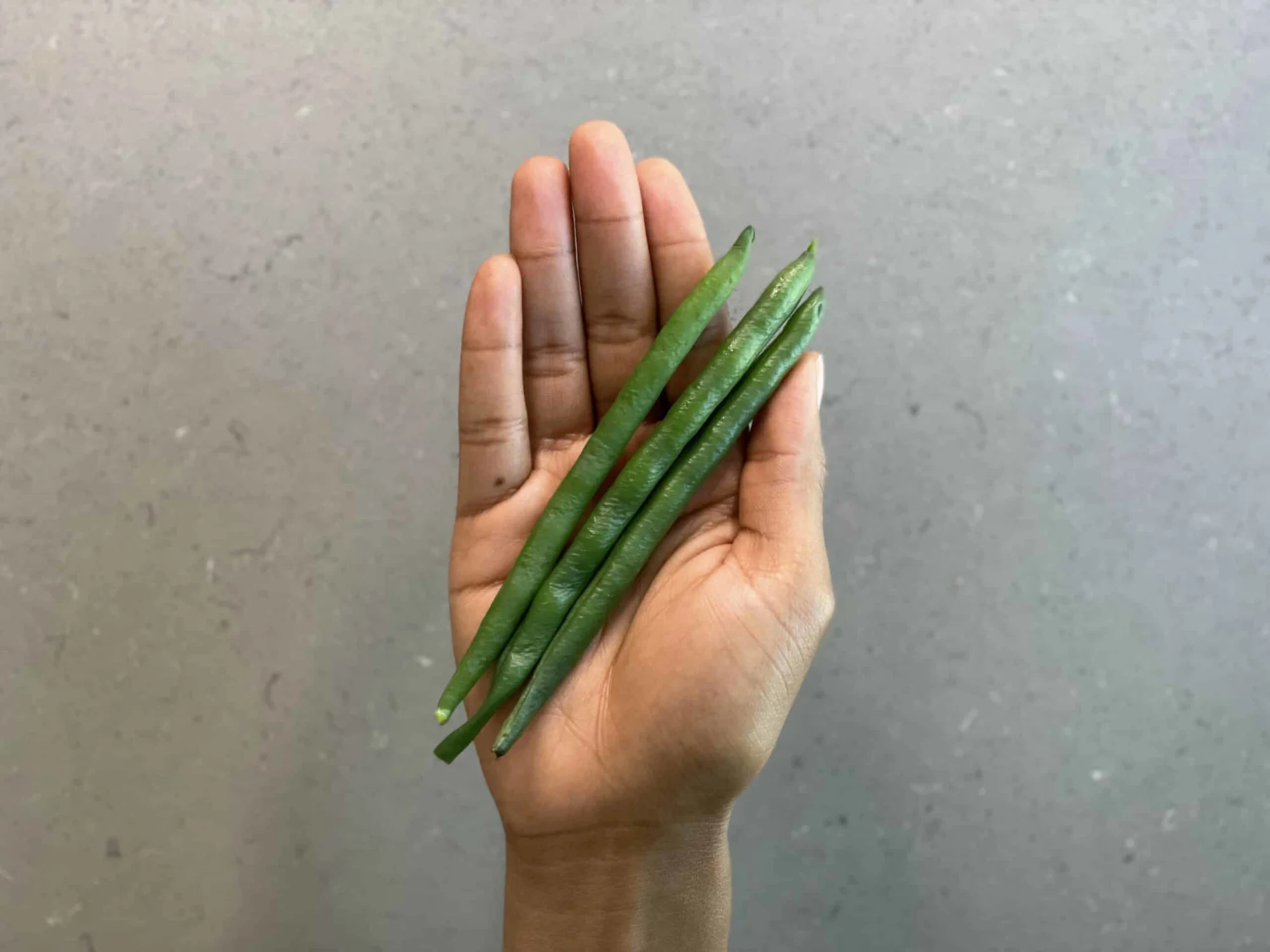
Offer cooked green beans in their whole form (a whole bean, uncut is best). At this age, whole bean pods may be safer for babies than pre-cut green beans. Whole bean pods are also easier for the baby to grasp. As they munch, their gums smash the pod and reduce its roundness, while small pieces of pre-cut green beans could be more likely to be accidentally swallowed whole. If you’d like to work the fine motor skills required for utensils, raw green beans can be excellent “spoons” or vehicles to practice self-feeding a pureed texture (like hummus). While baby won’t consume the green bean itself when used this way (as raw green beans require strong jaw control and for most babies, teeth, to break through the skin), they are fantastic for learning the skills of scooping.
12 months old +:
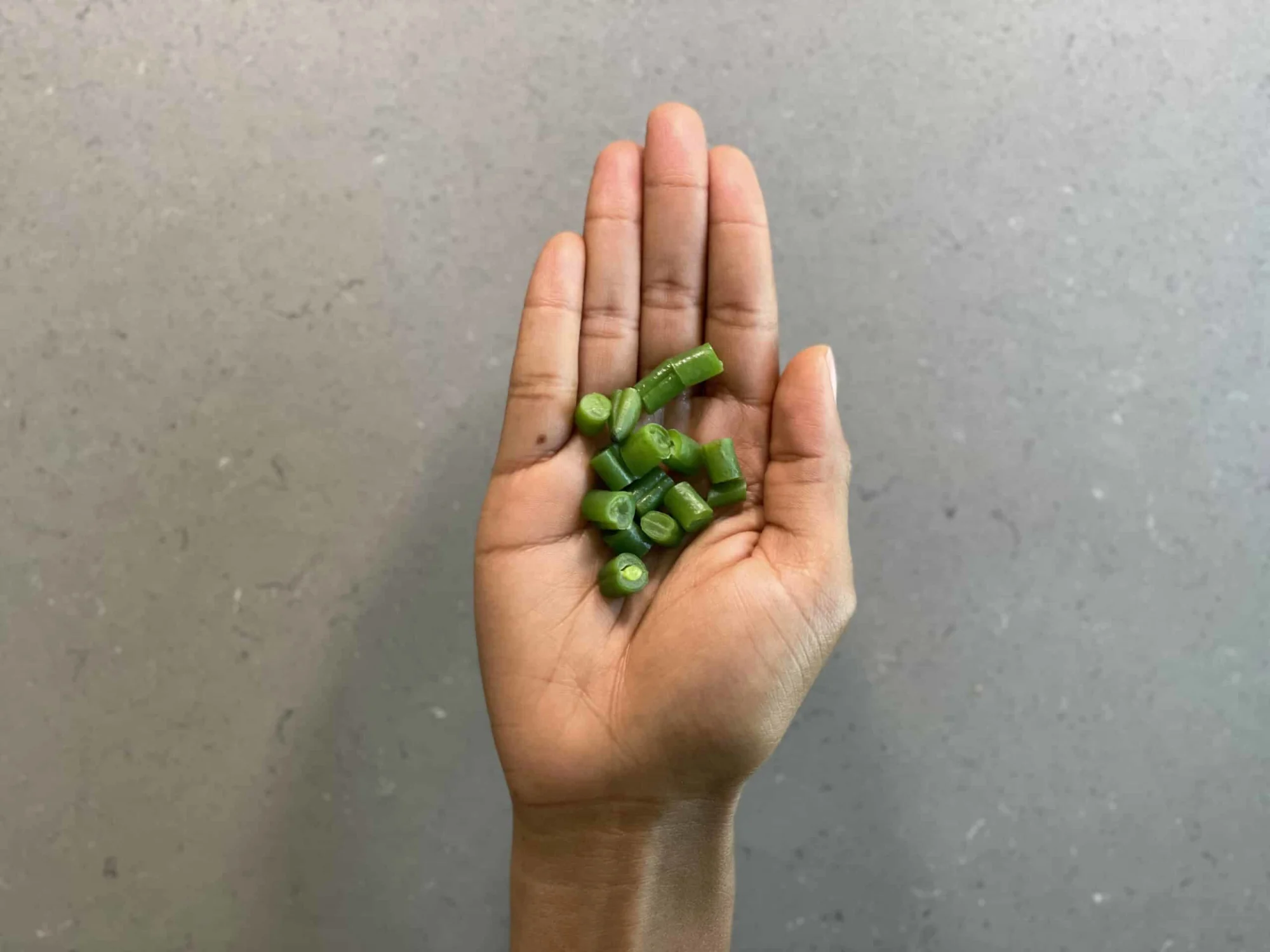
Offer bite-sized pieces of cooked green beans. This is also a great time to practice with forks and green beans spear quite nicely!
18 months old +:
Continue to offer bite-sized pieces of cooked green beans as finger food or serve with a fork but reduce the cooking time to acclimate the child to chewing tougher foods. You can also serve whole green beans with a dip.


Written by
Expert Tips Delivered to Your Inbox
Sign up for weekly tips, recipes and more!
The content offered on SolidStarts.com is for informational purposes only. Solidstarts is not engaged in rendering professional advice, whether medical or otherwise, to individual users or their children or families. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or your medical or health professional, nutritionist, or expert in pediatric feeding and eating. By accessing the content on SolidStarts.com, you acknowledge and agree that you are accepting the responsibility for your child’s health and well-being. In return for providing you with an array of content “baby-led weaning” information, you waive any claims that you or your child may have as a result of utilizing the content on SolidStarts.com.